Software as a service (SaaS) is a model where a third-party provider hosts the infrastructure and applications and make them available through the Internet. This model leverages on web-based software and on-demand applications that run centrally on the server of the provider, while the company purchasing the service will use those applications based on need and without the upfront cost. SaaS is a subcategory of a broader phenomenon and industry, based on cloud services. This also comprises other models like IaaS (infrastructure as a service) and PaaS ( platform as a service).
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Definition | SaaS (Software as a Service) is a cloud computing model that delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Instead of purchasing and installing software on individual computers or servers, users access and use the software hosted by a third-party provider. SaaS applications are typically accessed through web browsers, and users pay a recurring fee for access to the software, which is hosted and maintained by the SaaS provider. This model has gained popularity due to its cost-effectiveness, scalability, and ease of maintenance. |
| Key Characteristics | – Accessibility: SaaS applications are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, making them highly convenient for remote work and collaboration. – Subscription-based: Users pay a recurring subscription fee, often on a monthly or annual basis, rather than making a one-time software purchase. – Automatic Updates: SaaS providers handle software updates, ensuring users have access to the latest features and security patches. – Scalability: SaaS solutions can easily scale to accommodate the needs of small businesses or large enterprises. – Multi-Tenancy: SaaS providers typically serve multiple customers from a shared infrastructure, improving resource efficiency. |
| Benefits | – Cost-Efficiency: SaaS eliminates the need for upfront software purchase costs, hardware investments, and ongoing maintenance expenses. – Accessibility: Users can access SaaS applications from various devices, fostering flexibility and remote work capabilities. – Automatic Updates: SaaS providers handle software updates, reducing the burden on IT teams and ensuring security. – Scalability: SaaS solutions can grow with the business, allowing organizations to add or reduce users and features as needed. – Vendor Expertise: SaaS providers specialize in maintaining and securing software, leveraging their expertise for users’ benefit. |
| Challenges | – Data Security: Storing data in the cloud raises concerns about data security and privacy. – Internet Dependency: SaaS applications require a stable internet connection; downtime or connectivity issues can disrupt work. – Customization Limitations: SaaS solutions may have limitations on customization compared to on-premises software. – Vendor Lock-In: Migrating away from a SaaS provider can be complex and costly due to data and integration dependencies. |
| Applications | – SaaS is used across various industries for a wide range of applications, including customer relationship management (CRM), human resources management, project management, accounting, and collaboration tools. – It is also commonly used for web-based email services, like Gmail, and file storage and sharing, such as Dropbox and Google Drive. |
Table of Contents
The software industry before the internet
The main rule of software applications between the 1970s and 1980s was centralization. In short, a company provided a centralized mainframe-based system. At that stage company needed massive resources to install, manage, and maintain the software and the hardware infrastructure required to run those applications.
That implied a high risk and expense from businesses willing to implement those solutions at the enterprise level. That means a software market only available to large corporations with large budgets.
That changed in the late 1990s when an organization could centrally run, maintain and operate the hardware and software, while any company, small or large could plug in any device to access the applications and services.
That also implied the need for more computational power. Thus, as computers got more powerful. And the internet faster, those applications could finally be run by any organization to automate and improve their services. Things like the difficulty of deployment and high costs of ownership made it impossible for small businesses to take advantage of that technology.
When the on-demand becomes possible
The internet has opened up new business models, especially in the media industry. Where content could be consumed at the fixed schedule (think of TV and Radio) with the Internet, higher computing power, lower infrastructural costs, it becomes finally possible to consume content on-demand.
Companies like Netflix, Spotify, and many others have become the rule. Those business models make it possible for small organizations to run applications to automate their marketing processes at little cost.
This is a paradigm shift, as finally companies of any size could use applications once used only by Fortune 500 companies, all becomes outsources, scalable and tailored to the business operations.
The rise of the cloud economy
Source: financesonline
After the success of a few large players that reached billion in market capitalization, more and more startups joined in. As of the time of this writing, thousands of small companies around the world compete to offer SaaS solutions for any corporate need a company might have. But most of all from healthcare, legal, fintech, transportation and many others provide services based on the cloud.
Other large tech companies, like Amazon, Microsoft, Google and IBM are competing to dominate the cloud space:
It all started from the CRM industry
One of the companies that lead the way in the SaaS industry was Salesforce. That is a CRM application (customer relationship management) which for a monthly fee allows automating internal processes of small and large organizations. It is worth then to look at the player the opened up the way to this industry.
SaaS origin story: Salesforce
When we started the company in 1999, we had a vision that businesses would move to the cloud and subscription-based services. Salesforce led the industry as the first to bring cloud, social and then mobile to CRM.
Marc Benioff, founder of Salesforce, incorporated the company in Delaware in February 1999 and introduced its service offering in February 2000. The aim was clear, to offer a hosted service at low-cost, easy-to-use and quick to deploy the application.
This also implied a high level of customization, integration with other software applications. While this idea might seem trivial today, it was quite visionary back then. Indeed, before a concept like that would be successful, it also needed ecosystems to be built around the cloud. Before this concept would take off would take a few years.
Salesforce business model today
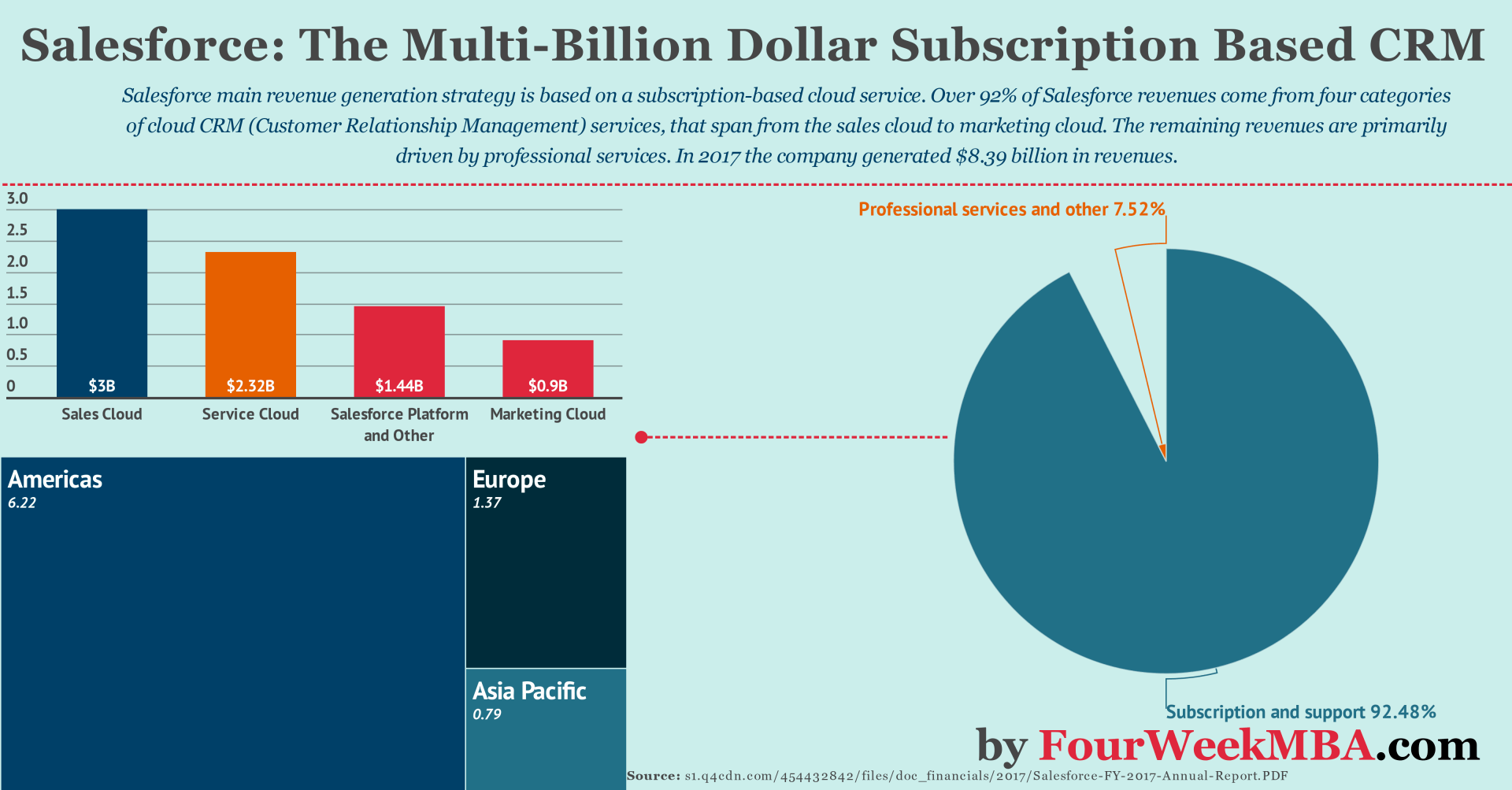
With a subscription-based business model, Salesforce has finally been able to build a multi-billion company that in 2018 surpassed the ten billion dollar mark in revenues.
The company also reached profitability in 2017, with $179 million in net profit and $127 million as of January 2018.
Those results have been possible thanks to the ecosystems that have finally been built around the cloud applications.
The power of ecosystems
Salesforce integrations capabilities
The key ingredient of SaaS services is that instead of installing and maintaining software, you can access it via the Internet, freeing the company for software and hardware maintenance costs.
However, a lack of other tools that could be integrated with the cloud solution still made it relatively valuable.
Think of the case of a company that had built several systems to collect the data of its customers, each relying on a different logic and framework. That data would be valuable as soon as it got offered within the context for which it has been thought.
However, with the rise of cloud computing and SaaS services all over the world, integrations have become the norm.
In short, a company can finally go on Salesforce or any other cloud service and find countless numbers of applications that can be integrated. While this might seem trivial at first sight, it is also what had made this industry finally viable.
Key Highlights
- SaaS Model: SaaS is a model where a third-party provider hosts infrastructure and applications on the internet. Users access these applications on-demand without the upfront costs associated with traditional software deployment.
- Pre-Internet Software Industry: Before the internet, software applications were centralized and required significant resources to install, manage, and maintain. This made them accessible only to large corporations with substantial budgets.
- Internet Revolution: The internet revolution of the late 1990s allowed centralized running, maintenance, and operation of software and hardware. This reduced costs and barriers to entry, making software accessible to companies of all sizes.
- On-Demand Consumption: With increased computational power and faster internet, on-demand consumption of content and services became possible. This led to the rise of models like Netflix and Spotify.
- Paradigm Shift: SaaS brought a paradigm shift, enabling organizations of any size to use applications once available only to large corporations. This made applications outsourced, scalable, and tailored to specific business needs.
- Cloud Economy: The success of SaaS giants led to the rise of a cloud economy. Numerous startups now compete to offer SaaS solutions across various industries, including healthcare, legal, fintech, and transportation.
- Major Players: Besides startups, tech giants like Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and IBM compete to dominate the cloud space.
- SaaS Pioneer: Salesforce: Salesforce, founded in 1999 by Marc Benioff, is a notable pioneer in the SaaS industry. It introduced cloud, social, and mobile aspects to CRM (customer relationship management).
- Salesforce’s Business Model: Salesforce’s main revenue comes from subscription-based cloud CRM services. It generated billions of dollars in revenues and achieved profitability.
- Ecosystems and Integrations: Ecosystems have been built around cloud applications, enabling seamless integrations and enhancing the value of SaaS services.
Case Studies
| SaaS Company | Description | Key SaaS Product(s) | Achievements and Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salesforce | A leading CRM software provider. | Salesforce CRM, Sales Cloud, Service Cloud | Pioneered cloud-based CRM, revolutionizing customer relationship management. Salesforce has become a global leader in the SaaS industry, helping businesses manage customer interactions and data effectively. |
| Slack | A collaboration and communication platform. | Slack (Messaging and Collaboration) | Transformed workplace communication with real-time messaging and integrations. Acquired by Salesforce, reinforcing the importance of collaboration in modern work environments. |
| Zoom Video Communications | A video conferencing and communication platform. | Zoom Meetings, Zoom Phone | Experienced explosive growth during the COVID-19 pandemic, becoming a household name for virtual meetings and webinars. |
| Dropbox | A file hosting and cloud storage platform. | Dropbox Business, Paper, HelloSign | Simplified file sharing and collaboration, serving individuals and businesses. Has millions of users worldwide and has expanded its offerings to include productivity tools. |
| Adobe | A software company offering creative and marketing solutions. | Adobe Creative Cloud, Adobe Marketing Cloud | Successfully transitioned from traditional software to cloud-based subscriptions, offering creative and marketing tools as services. |
| HubSpot | A marketing, sales, and customer service platform. | HubSpot Marketing Hub, Sales Hub, Service Hub | Pioneered inbound marketing and sales automation for businesses of all sizes. Helped companies attract, engage, and delight customers. |
| Zendesk | A customer service and engagement platform. | Zendesk Support, Zendesk Chat, Zendesk Sell | Streamlined customer support and engagement processes, enabling businesses to provide better service. |
| Shopify | An e-commerce platform for online businesses. | Shopify (E-commerce) | Empowered entrepreneurs and businesses to create online stores and sell products efficiently. Experiencing significant growth in e-commerce. |
| Twilio | A cloud communications platform. | Twilio API, Twilio Flex | Enabled developers to build communication applications with ease, powering SMS notifications, voice calls, and more for businesses. |
| Box | A cloud content management and file sharing platform. | Box (File Sharing and Collaboration) | Streamlined document collaboration and storage for businesses, with a focus on security and compliance. |
| DocuSign | An electronic signature and agreement platform. | DocuSign eSignature | Simplified document signing processes, facilitating digital transactions and agreements. |
| ZoomInfo | A B2B contact and account information platform. | ZoomInfo (Contact and Account Data) | Provides valuable business contact and account data for sales and marketing teams. |
| ServiceNow | A digital workflow and IT service management platform. | ServiceNow IT Service Management (ITSM) | Streamlined IT services and workflows for enterprises, enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction. |
| Atlassian | A team collaboration and productivity software company. | Jira, Confluence, Trello, Bitbucket | Empowered teams with software tools for project management, development, and collaboration. |
| Slack (formerly Trello) | A team collaboration and productivity platform. | Trello (Project Management) | Simplified project management and task tracking, improving team productivity. |
| Salesforce Marketing Cloud | A marketing automation and analytics platform. | Salesforce Marketing Cloud | Enabled businesses to create personalized marketing campaigns and analyze customer data. |
| SurveyMonkey | An online survey and research platform. | SurveyMonkey (Survey Software) | Facilitated online surveys and market research, collecting valuable insights for organizations. |
| Shopify Plus | An enterprise-level e-commerce platform. | Shopify Plus (Enterprise E-commerce) | Provided scalable e-commerce solutions for large businesses, catering to their unique needs. |
| Slack (formerly HipChat) | A team collaboration and chat platform. | HipChat (Team Chat) | Enhanced team communication and collaboration with real-time chat. |
| Workday | A cloud-based human capital management platform. | Workday HCM (Human Capital Management) | Streamlined HR and finance processes for organizations, improving workforce management. |
| Intuit QuickBooks | A financial management and accounting software. | QuickBooks Online (Accounting Software) | Simplified accounting and financial management for small businesses and freelancers. |
| Zoom Webinar | A webinar and virtual event platform. | Zoom Webinar | Enabled businesses to host virtual events, webinars, and conferences with interactive features. |
| Shopify POS | A point-of-sale system for retail businesses. | Shopify POS (Point of Sale) | Streamlined in-store sales and inventory management for retailers. |
| Microsoft 365 (formerly Office 365) | A suite of productivity tools. | Microsoft 365 (Office Applications) | Offered cloud-based versions of popular productivity software, enabling collaboration and remote work. |
| Wix | A website builder and hosting platform. | Wix (Website Builder) | Empowered individuals and businesses to create professional websites without coding skills. |
| Freshworks | A customer engagement and support platform. | Freshdesk, Freshsales, Freshservice | Simplified customer support, sales, and IT service management for businesses of all sizes. |
| Slack (formerly Asana) | A task and project management platform. | Asana (Task and Project Management) | Streamlined task management and project collaboration, improving team productivity. |
| DocuWare | A document management and workflow automation platform. | DocuWare (Document Management) | Digitized document processes and workflows, enhancing efficiency and compliance. |
| Zoho | A suite of cloud-based software applications. | Zoho CRM, Zoho Books, Zoho Desk | Provided a wide range of business software solutions, including CRM, accounting, and customer support tools. |
SaaS KPIs and Core Functions
Net Promoter Score

Innovation Funnel

Sales Funnels vs. Flywheels

Engines of Growth

Outside Sales

Inside Sales

Freemium Business Model

Freeterprise Business Model

IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS

C3.ai Business Model

Related Business Model Types
Platform Business Model

Marketplace Business Model

Network Effects

Asymmetric Business Models

Attention Merchant Business Model

Wholesale Business Model

Retail Business Model

B2B2C

Crowdsourcing Business Model

Open-Core Business Model

Open Source vs. Freemium

Freemium Business Model

Freeterprise Business Model

Franchising Business Model

Handpicked case studies:
- The Power of Google Business Model in a Nutshell
- How Does Google Make Money? It’s Not Just Advertising!
- How Does DuckDuckGo Make Money? DuckDuckGo Business Model Explained
- How Does Twitter Make Money? Twitter Business Model In A Nutshell
- How Amazon Makes Money: Amazon Business Model in a Nutshell
- How Does Netflix Make Money? Netflix Business Model Explained
- DuckDuckGo: The [Former] Solopreneur That Is Beating Google at Its Game
Other business resources:
- Successful Types of Business Models You Need to Know
- The Complete Guide To Business Development
- Business Strategy: Definition, Examples, And Case Studies
- What Is a Business Model Canvas? Business Model Canvas Explained
- Blitzscaling Business Model Innovation Canvas In A Nutshell
- What Is a Value Proposition? Value Proposition Canvas Explained
- What Is a Lean Startup Canvas? Lean Startup Canvas Explained
- What Is Market Segmentation? the Ultimate Guide to Market Segmentation
- Marketing Strategy: Definition, Types, And Examples
- Marketing vs. Sales: How to Use Sales Processes to Grow Your Business
- How To Write A Mission Statement
- What is Growth Hacking?
- Growth Hacking Canvas: A Glance At The Tools To Generate Growth Ideas














